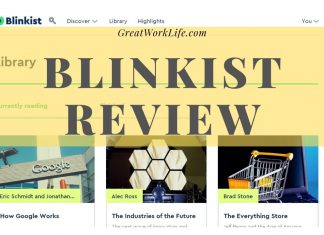
The basic economic principle of supply and demand shapes stock prices. When more people want to buy a stock than sell it, the price goes up. When more people want to sell than buy, the price drops. This simple idea drives the complex world of stock trading.
Many factors can sway the supply and demand for stocks. These include a company’s financial health, market trends, and even world events. Investors often look at earnings reports and economic indicators to decide whether to buy or sell. Understanding these forces can help explain why stock prices move the way they do.
What Determines Stock Prices?
Stock prices are set by the push and pull of buyers and sellers in the market. I’ve seen how they shift based on new info and changing views about a company’s future. When more people want to buy than sell, prices climb. When more want to sell, prices drop.
Key factors that move stock prices include:
• Earnings reports
• Economic news
• Government policies
• Central bank decisions
The initial public offering (IPO) sets a stock’s first trading price. After that, supply and demand take over. A company’s share price can swing rapidly as traders react to fresh data and events.
What Influences a Stock’s Price?
Supply and demand play a big role in stock prices. When more investors want to buy a stock, its price goes up, and when more want to sell, it goes down.
Earnings per share (EPS) is another key factor. I’ve seen stocks jump after good earnings reports. The price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio helps investors judge if a stock is cheap or pricey.
Market sentiment affects prices, too. If investors feel good about a company, they may bid up its stock. Economic factors like interest rates and inflation matter as well. Company news, products, and profitability all impact stock prices.
Dividends
Dividends are a key part of stock investing. When a company pays dividends, it gives some of its profits to shareholders. This can make a stock more attractive to investors like me.
Dividend payments can affect stock prices. When a company announces a dividend, its stock price often goes up, which investors see as a sign of financial health. On the ex-dividend date, the stock price usually drops by about the amount of the dividend. For example, if a $50 stock pays a $2 dividend, it might open at $48 on that day. This makes sense, as the company is giving away some of its value.
Dividend yields can change as stock prices move. If a stock pays $1 per year in dividends and costs $25, its yield is 4%. If the price rises to $50, the yield drops to 2%, even though the dividend hasn’t changed. Companies that raise their dividends year after year are often seen as stable investments. These are called “dividend aristocrats,” and many investors seek them out.
But dividends aren’t always good. If a company pays too much in dividends, it might not have enough money left to grow the business. This could hurt the stock price in the long run.
I use TrendSpider to help me analyze dividend stocks. It’s a powerful tool that uses AI to spot patterns in stock charts.
How are stock prices determined in real-time?
Stock prices change constantly during trading hours. Many factors influence these real-time price movements. The most important are bid and ask prices, trading volume, and market conditions. Breaking news about a company can also cause quick price changes.
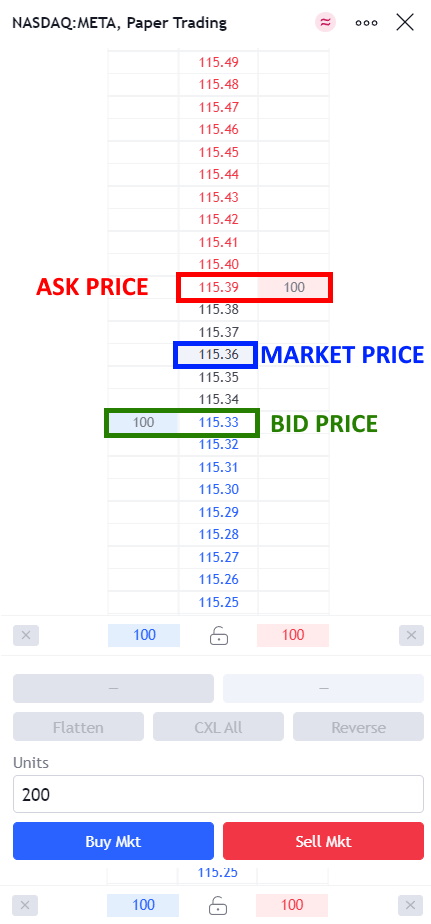
The Impact of Bid/Ask Prices on Stock Value
Bid and ask prices are key to setting a stock’s price. The bid is what buyers will pay, while the ask is what sellers want. When more people want to buy than sell, the price goes up, and when more want to sell, it drops.
I’ve seen this play out on Wall Street many times:
- High demand = Higher bids = Price rises
- Low demand = Lower asks = Price falls
This image shows how it works:
Volume
Trading volume plays a big role in stock prices. It shows how many people are buying and selling a stock. When lots of shares are traded, it means there’s high interest. This can push prices up or down quickly. Big investors often watch volume closely. They use it to spot trends and make choices. High volume with rising prices is a good sign. It means more buyers than sellers, which can make the stock even more attractive.
Volume also affects how easy it is to buy or sell stocks. More volume usually means better liquidity, which is important for traders who need to move quickly in and out of positions.
Here’s a simple breakdown of what volume can tell us:
- Low volume: Not much interest
- High volume: Lots of interest
- Rising volume and price: Bullish sign
- Falling volume and price: Bearish sign
News
Financial news can really shake up the stock market. Big events like earnings reports or FDA approvals can send stocks soaring or plummeting. Traders who catch wind of these developments first often have an edge. Take company buyouts, for example. When a firm gets acquired, its stock price usually jumps as investors expect bigger profits down the road. On the flip side, bankruptcy filings or mass layoffs tend to tank share prices.
It’s not just company-specific news that matters. Broader economic reports can move entire sectors or even the whole market. Interest rate changes, job numbers, or GDP data can spark big swings. Investors must stay informed about financial news. However, it’s important to separate signal from noise. Not every headline is worth trading on.
✂ Save 37% on Benzinga Pro Real-time News & Options Mentor ✂
Market Conditions
Market conditions play a big role in stock prices. When things are good for business, stocks often go up. This can mean low interest rates, fewer rules for companies, and lots of people buying stuff. If most stocks are doing well, it can lift other stocks too. But if the market is having a hard time, many stocks might drop.
I’ve seen how economic growth and the overall business climate can affect stock prices. Political risks can also cause prices to fluctuate more.
Does exercising options affect stock price?
When people exercise stock options, it can impact the stock price. I’ve seen this happen when many employees cash in their options at once. They buy shares at the set price, which increases demand. This extra buying can push the stock price up. Options trading also affects prices in other ways. If a stock starts falling fast, investors who sold put options might buy shares to limit their risk. This can create more demand and slow the price drop.
Companies often use stock options to motivate executives and workers. When these options mature, it can lead to lots of buying and selling. This activity can move the stock price up or down.
Here’s a simple example:
- Company XYZ gives 1000 employees options to buy stock at $50
- Stock price rises to $75
- Employees exercise options, buying at $50
- They might then sell at $75 for a quick profit
- This selling pressure could push the price down
Options don’t directly set stock prices, but they can influence them through these buying and selling patterns.
Understanding Market Capitalization
Market capitalization measures a company’s value in the stock market. It’s calculated by multiplying the total number of outstanding shares by the company’s current stock price. Large-cap companies often attract more attention from investors. I’ve noticed that many see these firms as more stable and established. This perception can lead to increased demand for their stocks, potentially driving up prices.
Index funds and ETFs play a big role, too. These investment vehicles often track market indexes, which typically include companies based on their market cap. When a company’s market cap grows, it might be added to an index, which can boost its stock price.
Tesla’s story is a great example. In 2013, its market cap grew enough to join the Nasdaq 100 index. After joining, Tesla’s stock price jumped from $4 to $12 in just a year—a 200% increase!
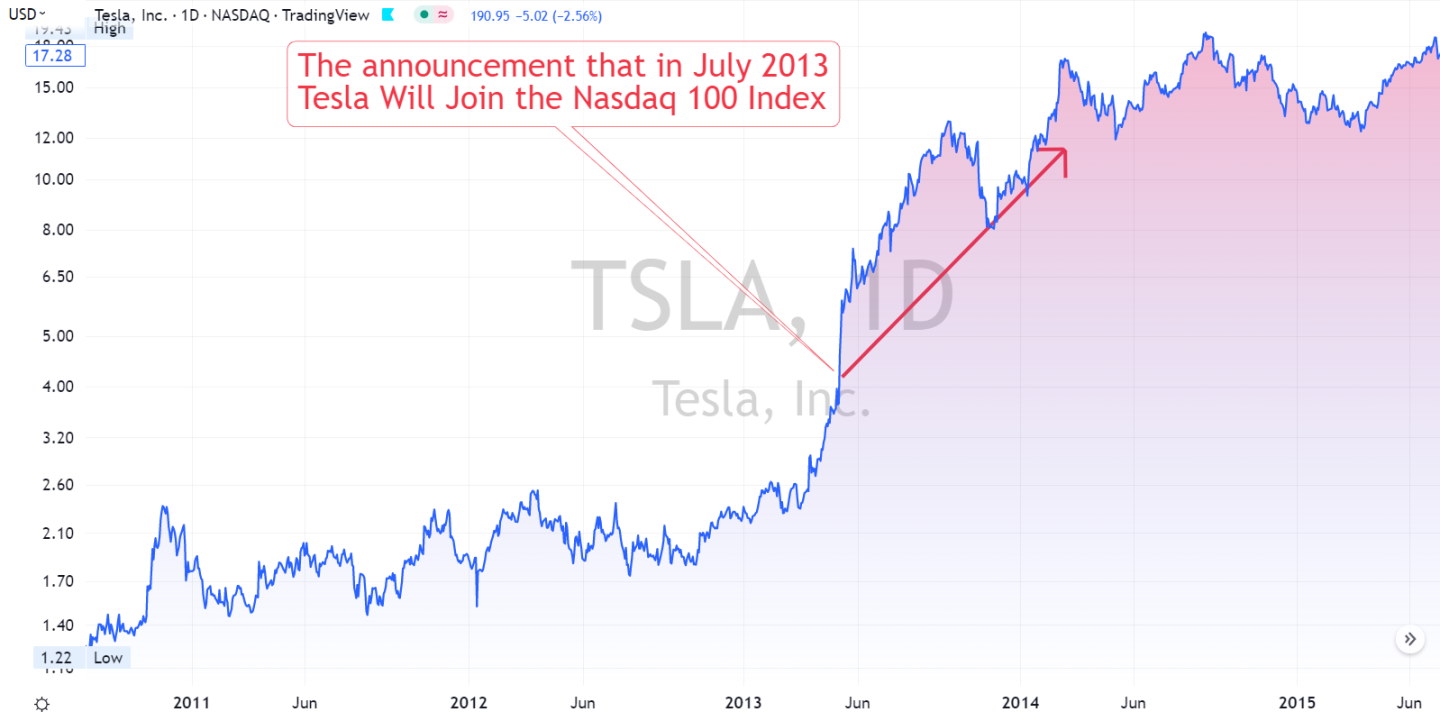
Why does the consumer price index affect stocks?
When the consumer price index (CPI) goes up, it often leads to a drop in stock prices. This happens because higher prices mean people spend more on everyday items, leaving less money for other purchases. Companies may raise their prices to cope with increased costs, which can hurt demand for their products.
The CPI is a key measure of inflation, tracking prices across various sectors like food, housing, and healthcare. When it rises, central banks often step in to cool the economy by raising interest rates. This can make borrowing more expensive for businesses, potentially cutting into their profits and making stocks less attractive to investors.
The Impact of Inflation on Stock Prices
I’ve seen that inflation can significantly impact stock prices. When prices go up across the board, companies often face higher costs for materials, labor, and transportation. This can eat into their profits if they can’t pass these costs on to customers.
Inflation also reduces money’s purchasing power. This means that $100 today might buy less in the future. For stocks, this can be a double-edged sword. Some companies might benefit from raising prices, but others might struggle if consumers cut back on spending.
Here’s a simple breakdown of how inflation can affect different types of stocks:
- Growth stocks: Often hit hard as future earnings are worth less
- Value stocks: May hold up better, especially if they pay dividends
- Commodity-related stocks: Can benefit from rising prices
It’s important to note that not all stocks react the same way to inflation. Some industries, like consumer staples or utilities, might be more resilient because people need their products regardless of economic conditions.
Looking at historical data can be helpful. For example, during periods of high inflation in the past, certain sectors like energy and materials have sometimes outperformed the broader market. However, past performance doesn’t guarantee future results.
Investors often look for ways to protect their portfolios from inflation. This might include buying stocks in companies with strong pricing power or those that benefit from rising prices. It’s always a good idea to diversify and consider how different economic scenarios might affect your investments.
TradingView gets my top rating! It’s hands down the best trading software out there, offering built-in broker integration, powerful backtesting tools, advanced scanners, and access to the world’s largest trading community. It’s a game-changer for traders at all levels!
What Impact Do Stock Prices Have on a Company?
Stock prices can have big effects on companies. A high stock price lets a company buy other businesses more easily and use its stock to make deals. However, a low stock price can cause problems. Other companies might try to buy them out, and investors may push for changes. When stock prices keep falling, it puts pressure on the company’s management. They may need to make changes to improve the business’s performance. This could mean new strategies or cutting costs. The stock price becomes a way to judge the company’s performance.
Dark Pools Explained
Dark pools are private stock exchanges where big investors trade stocks without immediately affecting prices. These hidden markets don’t have the same rules as public exchanges, which means less openness. This can lead to price manipulation. If I want to sell a lot of shares, I might use a dark pool to avoid tanking the stock price right away.

How Does the Stock Market Influence Housing Prices?
When stocks go up, home prices often follow. People have more money to spend when their investments do well. They’re more likely to buy houses, which pushes prices up.
It’s like a chain reaction:
- Stocks rise
- Investors feel richer
- More people can afford homes
- Housing demand increases
- Home prices go up
This link between stocks and houses shows how different parts of the economy are connected. When one area does well, it can boost others, too.
Is there manipulation in stock prices?
Stock price manipulation is a real concern in financial markets. While it’s illegal, various entities still find ways to influence stock prices for their gain. I’ve seen how companies, news outlets, central banks, and governments can all influence stock values.
Companies might spread false info about their prospects to boost their stock. News agencies can unknowingly share incorrect reports that sway investor decisions. Meanwhile, central banks use monetary policy to impact the economy, which then affects stocks. Lastly, governments can inject money into the system, lifting company profits and stock prices.
What drives stock prices up and down?
Stock prices move for many reasons. Individual investors buying and selling don’t solely cause changes.
Here are some key factors I’ve identified:
- Company performance
- Economic indicators
- Interest rates
- Market sentiment
- News and events
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is one economic indicator that can really move stocks. When the CPI goes up, it often means higher inflation.
This can lead to:
- Higher costs for companies
- Reduced consumer spending
- Potential interest rate hikes
These effects can push stock prices down. On the flip side, low inflation can boost stock prices.
I’ve seen how the Federal Reserve uses interest rates to fight inflation.
When rates go up:
- Borrowing becomes more expensive
- Consumer spending may slow
- Company profits can decrease
This can put downward pressure on stocks. But it’s not always simple. Sometimes, higher rates can signal a strong economy, which might actually lift stock prices.
Dark pools are another way stock prices can be manipulated. These are private exchanges where large trades happen out of public view. They can:
- Hide big trades from the market
- Potentially move prices when trades are revealed
- Make it harder for regular investors to see what’s really going on